News
A Brief Introduction to X-ray Imaging
1st Jun, 2020
A Brief Introduction to X-ray Imaging: First discovered by Roentgen, X-rays have been a cornerstone technology in medical diagnostics, helping clinicians diagnose a wide range of immediate and underlying health issues in patients. Yet this familiar technology is useful for a broad application base beyond medical radiography interventional surgery and CT applications.
X-ray imaging covers a wide energy range, from gamma (high energy X-rays produced by linear accelerators in MeV range) to hard X-rays (100s of keV range produced by sealed tubes) and soft X-ray rays (100s of eV range) as produced in modern synchrotron sources or Extreme UV semiconductor machines which produce nanometer-scale integrated circuits.
Understanding X-ray Imaging: The Basics
In general, X-ray imaging techniques are based on absorption contrast, which means that X-rays are attenuated by materials with known density according to Beer’s law. Using the right energy range is therefore crucial for delivering the right contrast within a given material of biological samples. Once the optimum X-ray energy range has been set out, we must propose a detector with optimized detective quantum efficiency. We distinguish two types of detectors, those capable of capturing X-rays directly into a semiconductor material which will convert incoming photons into an electron charge that can be digitized, or indirectly with a scintillator material with incoming X-rays being converted into visible photons which are then collected by a CMOS sensor. The intrinsic contrast delivered by biological tissues/organs or materials will depend on both abilities to select the right energy range as well as detecting most of the incoming photons into signal well above the detector noise floor.
Key Applications of X-ray Imaging
The most immediately recognizable application of X-ray imaging is of course medical radiography. Yet the power and precision offered by this innovative technology are applicable to a much wider market cross-section in synchrotrons and laboratories. A short selection of potential areas of use include:
- Coherent diffraction imaging
- Contrast imaging
- Crystallography
- Microtomography
- Phase-contrast imaging
- Printed circuit board (PCB) testing
- Radiography
- Source qualification
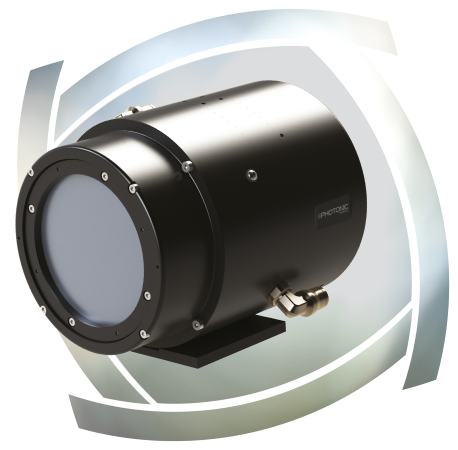
X-ray Imaging with Photonics Science
Photonic Science specializes in the development of advanced X-ray cameras solutions for medical and industrial radiography applications, supplying safe and efficient instrumentation for high-resolution X-ray imaging. Our products include:
- X-ray FDS Detector
- X-ray sCMOS 4MP Detector
- X-ray sCMOS 16MP Detector
- X-ray Laue Back-Scattered Camera
If you would like more information about our comprehensive range of X-ray imaging products, simply contact a member of the team today.